A Brief Introduction to FMCG
Author: Celia| Keywords chosen by Celia

Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) refers to the daily necessities with a consumption cycle no more than 10 weeks. It contains foods, drinks, toiletries, household items and so on. Given the competitive market, Brand loyalty is the key channel for maximum market benefits for FMCG.
As one of the largest industry all over the world, online shopping has been the most profitable sales channel for FMCG.

What is FMCG?
FMCG means daily goods bought frequently by consumers, it gains profits and values from selling in quantities. FMCG also called PMCG (Packaged Mass Consumption Goods), by definition, products will be sold after packaging into units. Package, branding as well as democratization affect a lot on it.
FMCG needs basic industry principle, more focuses on details, innovative products, promotion and brand maintain as well. There exists a “three month-period” for FMCG, which indicates that if a competitor get an outbreak for quantities during three months, you will be defeated by it.
A correspond concept for FMCG is DCG (Durable Consumer Goods), which are those with longer life cycle with great investment, such as household appliances, furniture, cars and so forth.

What are FMCG’s features?
1. Convenience. Consumers can find and buy them easily near their places.
2. Visualized products. It’s easy for consumers to get affected by the store atmosphere when doing shopping.
3. Low brand loyalty. Consumers may change their brands among similar products.
4. Lack of changes of nature.

What are their basic properties?
1. Short Turned-Around-Time for products.
2. Wide user groups.
3. Similar product usage.
4. Selling by means of branches or agents.
The above-mentioned features and properties decide the purchase habits for FMCG: simple, fast, impulsive and emotional.
FMCG has achieved success in the past decades. In 2010, this industry has created 23 brands in the Top 100 all over the world. In addition, the total return to shareholders recorded a growth of about 15%, next only to the material industry.

Five common business models for FMCG
1. Brand building & product creation
A brand’s success depends on its product creation. FMCG got 25% higher gross profit margin than that of other brand competitors in 2018, according to a research by McKinsey.
2. Good relationship with retailers
The close cooperation with partners enables FMCG companies to obtain expansive distribution channels, with which products are quickly introduced to consumers.
3. International business expansion
There is no doubt that international business expansion helps FMCG companies to get great profits. The growth of consumption levels increased the income for FMCG industry for almost 75% in the past decade.
4. Improvement of operating modes
For many enterprises, centralized operation is the most common used mode. Keep improving operating modes is useful for FMCG enterprises to manage their fees to 4% to 6% of income.
5. M&A to consolidate market
Through M&A, the further expansion of new brands and product categories contribute to getting more market shares for FMCG industry.

 Piece Together the Clues with XIMIVOGUE Conan Puzzle and Fridge Magnets
Piece Together the Clues with XIMIVOGUE Conan Puzzle and Fridge Magnets
 Make Journaling Mistakes Beautifully with XIMIVOGUE Erasable Gel Pens
Make Journaling Mistakes Beautifully with XIMIVOGUE Erasable Gel Pens
 XIMIVOGUE Store in Ljubljana Gains Attention from Slovenian Media
XIMIVOGUE Store in Ljubljana Gains Attention from Slovenian Media
 Elevate Your Space with XIMIVOGUE Throw Pillows
Elevate Your Space with XIMIVOGUE Throw Pillows
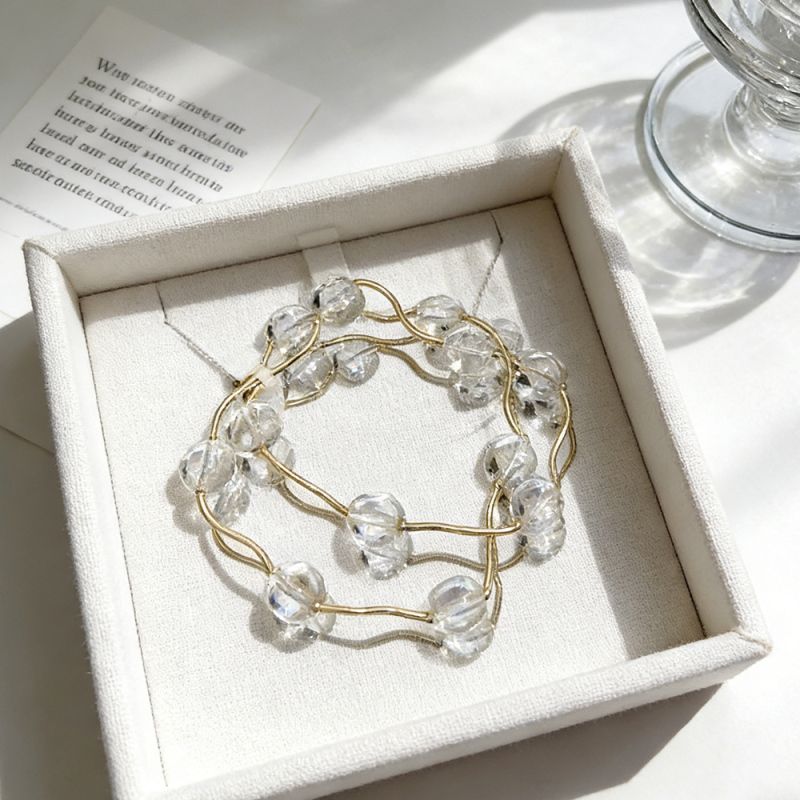 XIMIVOGUE Spring Bracelets That Breathe New Life
XIMIVOGUE Spring Bracelets That Breathe New Life